To install Radmin v2.2 on Windows x64 edition:
First install Radmin Server v2.2 on your computer.
Due to how Microsoft has changed its handling of 32bit applications under XP 64bit, the default installer for Radmin does not work properly.
When the installer says to put the r_server into system32, Microsoft re-directs the file to C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64. Unfortunately, Microsoft was not also smart enough to intercept the service creation call and change that path as well. Evidently on the X64 OS, the service has to be in the C:\Windows\SysWOW64
The following information is to be used at your own risk.
Go to Start -> Run -> Type Regedit and press “Enter” button.
Go to [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\r_server]
Look for the Imagepath string that looks like "c:\windows\system32\r_server.exe /service" Change the “C:\Windows\System32” to “C:\Windows\SysWOW64”
Use F3 to search for any occurrences and then you can start your service just fine.
Go to Start -> All Programs ->Remote Administrator v2.2 -> Start Remote Administrator server.
My experience has been on Microsoft® Windows® Server 2003 Standard x64 Edition Version 5.2.3790 Service Pack 1 Build 3790 that the standard install did exactly what it was expected to, placed the r_server.exe in the c:\windows\SysWOW64 directory and correctly installed the service to the same path, but it would not start nor did it generate any logs or errors other than the service reported that it did not start in the time expected.
Evidently on the X64 OS, the service has to be in the C:\Windows\SysWOW64 or it will not start. Once I made the coresponding change to the registry, r_server worked as expected.
Cheers!
Tuesday, October 09, 2007
Remote Administrator v2.2 on Windows Server 2003 Standard x64 Edition
File (5GB) Copy Error to external hard drive
Check out the hottest 2008 models today at Yahoo! Autos.
Wednesday, September 26, 2007
Backup Exec Backup Job Fail due to an Open File
"Corrupt data encountered" (a000fe36 HEX or e000fe36 HEX) is reported when a backup job fails.
Details:
Final Error Code: a000fe36 HEX (0xa000fe36 HEX) or e000fe36 HEX (0xe000fe36 HEX)
Final Error Description: "Corrupt data encountered. See the job log for details."
Final Error Category: Resource Errors
Error Text In Job Log: "Warning: %File% is a corrupt file. This file cannot verify."
This error occurs when VERITAS Backup Exec (tm) attempts to back up a file that is in use by another application or user.
Backup Exec may back up partial data from such a file, but when it is not able to continue the backup of the file, Backup Exec marks the file on the tape as corrupt (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Note: The error refers to the instance of the file on the tape. The file on the hard disk drive may be intact.
Backup Exec Advanced Open File Option (AOFO) can be used to avoid the error. The AOFO component of Backup Exec enables the functionality to perform a complete backup of files which are open through various applications. This is a "paid for" option.
If AOFO is not used, then the following are the workarounds to avoid the error:
1. Click Tools Options Properties Job Defaults Backup. Select Never under Open file backup when Advanced Open File Option is not used (Figure 2).
Figure 2
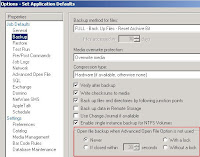
Select this option to have Backup Exec skip open files if they are encountered during the backup operation. A listing of skipped files will appear in the job log for the backup.
2. Close the respective files during backup
Monday, September 24, 2007
Recover Hard-Deleted Emails with DumpsterAlwaysOn option in Microsoft Outlook
In Microsoft Outlook, there are two types of delete actions: hard deletes and soft deletes. A soft delete is when an item is moved to the Deleted Items folder in the Microsoft Outlook mailbox; the deleted item can be recovered any time before the Deleted Items folder is emptied. A hard delete is when an item is deleted without first putting it in the Deleted Items folder. (Pressing Shift + Delete in Microsoft Outlook executes a hard delete.) Hard deletes also take place if the remote server uses IMAP and doesn't have a Deleted Items folder.
After a hard delete, you may still be able to recover mail items from an Exchange mailbox -- it depends on what the Exchange server's delete retention time is set for. Typically 14 days for emails, contacts or other items and 30 days for mailboxes. You can change the settings on EMC Server Configuration Mailbox Right-click Mailbox
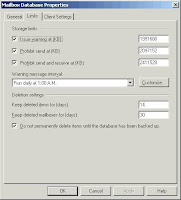
This functionality is typically only enabled for the Deleted Items folder. Items hard-deleted from Sent Items, Drafts, Outbox or Inbox are usually gone for keeps.
If you want to set delete-recovery for those folders, you need to edit the client registry accessing the Exchange server through Outlook:
- Open the registry.
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWARE\Microsoft\Exchange\Client\Options.
- Add a DWORD value named DumpsterAlwaysOn and set it to 1.
- Restart Microsoft Outlook to make the change take effect.
This option can also be rolled out as part of a policy change or made permanent through a .REG file.
Note that even with this option activated, Microsoft Outlook 98 will not support deletions from non-mail folders, such as Contacts and Notes. Microsoft Outlook 2000 and 2003, however, will allow non-mail deleted items to be recovered with this option enabled.
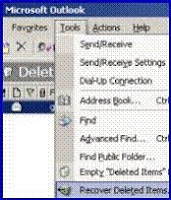
Recover Deleted Items in Outlook
Provided you configured the Windows Exchange mailbox store to hold deleted items, users can restore their own emails from within Outlook 2003. All they have to do is click on the Tools menu, and then select Recover Deleted Items from the drop down menu. See diagram opposite. Naturally, the user can select which emails to recover. Any emails that they select Outlook will miraculously move to the Deleted Items Folder. If the option Recover Deleted Items is deactivated, then go to Deleted Items folder and delete one email for which you already have a backup. After you delete one item, the recover deleted item would be visible with past deleted items.
Slightly surprisingly, users can also recover deleted items using Exchange 2003's Outlook Web Access. In this case, select Options (menu) and Recover Deleted Items is right at the bottom of the page.
Helpful Links:
http://www.computerperformance.co.uk/exchange2003/exchange2003_recovery_deleted_item.htm
http://searchexchange.techtarget.com/tip/0,289483,sid43_gci1024524,00.html
Saturday, September 22, 2007
Backup Exec 11D GRT for Exchange Server
-After performing the GRT backup to the specified B2d device run a duplicate job to tape in case the space used in the original B2d location may be needed at a later time
-If a Backup to tape must be used in conjunction with the GRT feature, make certain that there is sufficient disk space on a NTFS volume local to the media server to perform the restore operation. Disk space equivalent to the size of the database containing the item, or items, to be restored is required.
-If multiple non-concurrent restore operations of individual items may be required, and the GRT backup data was written to tape, consider performing a set copy operation of the data to a backup-to-disk folder prior to performing the initial restore operation. This will allow the use of dynamically created selections for individual items and will save a great deal of time in the event that multiple non-concurrent restore operations are required.
Be a better Globetrotter. Get better travel answers from someone who knows.
Yahoo! Answers - Check it out.
Friday, September 21, 2007
Video Series: Exchange 2007 SP1 Standby Continuous Replication (SCR)
Beta 2 of Service Pack 1 Exchange Server 2007 is available for public download and preview for MSDN and TechNet subscribers.
Following is a 5-part blogcast that takes us through the process of enabling SCR, monitoring SCR, and activating an SCR storage group copy using the Exchange Management Shell and other features, such as database portability.
http://msexchangeteam.com/archive/2007/09/13/447006.aspx
Wednesday, September 19, 2007
After performing a complete backup of a Microsoft Exchange 2007 Server, additional backups may fail with an AOFO initialization error.
aofo: initialization failure...0xe000fed1: an error occurred querying the writer status
Backup Exec 11d for Windows Servers version uses Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to perform backups of Exchange data. These backups initialize and run the Microsoft VSS provider and Exchange VSS writer which may not properly terminate after the backup job is complete. Once VSS has gotten into this state, backup jobs will fail with:
AOFO: initialization failure...0xe000fed1: an error occurred querying the writer status.
According to the Microsoft document listed below, possible workarounds include dismounting then mounting the Exchange databases using the Exchange Management Console or stopping and restarting the Microsoft Exchange Information Store service. Please see the Microsoft document for the details of these workarounds. In addition, the option of using Windows Backup (NTBackup) may be used as an alternative as well as it does not rely on VSS for Exchange backups.
Microsoft Knowledge Base Article - 930800:
Event ID 9840 is logged when a VSS backup operation fails in Exchange 2007
http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=930800
278212: "Final error: 0xe000fed1 - A failure occurred querying the Writer status" or "VSS Writer failed, but the operation can be retried (0x800423f3) State: Failed during freeze" occurs when backing up Exchange databases with AOFO and Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service.
http://support.veritas.com/docs/278212
Boardwalk for $500? In 2007? Ha!
Play Monopoly Here and Now (it's updated for today's economy) at Yahoo! Games.
Tuesday, September 18, 2007
Configure Backup Exec Service account to perform Exchange 2007 Mailbox Backup
Details:
In Exchange 2003, the following security roles were available through the Delegation Wizard in Exchange System Manager:
Exchange Full Administrator
Exchange Administrator
Exchange View Only Administrator
Exchange 2007 has the following predefined groups that manage Exchange configuration data:
Exchange Organization Administrators
Exchange Recipient Administrators
Exchange View-Only Administrators
Exchange Server Administrators
Perform the following in order to back up Exchange 2007 Database using Backup Exec:
Make sure that the Remote Agent for Windows Servers is installed on the Exchange server, if the Exchange server is not locally installed on the Backup Exec computer.
Ensure that the Backup Exec service account has Domain Admin and Local Administrative rights.
Verify that the Backup Exec service account mailbox is not hidden.
To configure Backup Exec service account, refer to the following instructions:
1. Go to Active Directory Users and Computers and go to the Users directory. Right-click on the Administrator account and select copy (see Figure 1) and create an account for BACKUP EXEC.
Figure1
2. Go to Services applet and stop all Backup Exec services. Then configure all the Backup Exec services with the new account just created (see Figure2).
Figure2
4. In the Exchange Management Console, select Organization Configuration. (see Figure 3)
Figure3
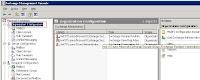
5. Right click on Organization Configuration and select Add Exchange Administrator. (see Figure 4)
Figure4

6. On the Add Exchange Administrator page, click Browse and select the user that you want to delegate control to.
7. Select the Exchange Server Administrator Role radial button. (See Figure 5)
Figure5
8. Click Add and under Select the server(s) to which this role has access select the servers to which you want to delegate control.(See figure 6)
Figure6
9. Click OK. Click Add.
10. On the Completion page verify that the delegation was successful and click Finish.
Related Documents:
243328: How to remove the "Hidden" attribute from Exchange 2000 and Exchange 2003 mailboxes so that the mailboxes will be available to the Global Address List for backup purposes http://support.veritas.com/docs/243328
287804: Symantec Backup Exec 11d for Windows Servers Sets the Standard for Exchange 2007 Server Data Protection http://support.veritas.com/docs/287804
Symantec Backup Exec 11D - Exchange 2007:- Access Denied
Results Found for Error Message: V-79-57344-33928
Items 1 to 11 of 11 by publish date.
290764: After upgrade to Backup Exec 11d for Windows Servers build 6235, attempt to access a public folder fails with the error: "V-79-57344-33928 - Access is denied" - 09/04/2007
289815: Access denied is reported while running backups to disk, or restores from tape, of Exchange 2003 from an x64 bit media server. - 08/13/2007
287464: A Backup Exec 11d Exchange Information Store (IS) backup to a Backup-to-Disk Folder fails with the error: '-546 The log file sector size does not match the sector size of the current volume. ' when the Granular Restore Technology feature is enabled. - 08/03/2007
289970: Backup of Information Store in Exchange 2007 fails with error "Unable to complete the operation for the selected resource using the specified options. The following error was returned when opening the Exchange Database file: '-514 The version of the log file is not compatible with the ESE version" - 07/26/2007
266178: "Access is denied" (a0008488 HEX or e0008488 HEX) is reported when a job fails - 07/24/2007
289649: Backup of Microsoft Exchange 2007 Information Store fails with error "V-79-57344-33928 - Access Denied. Cannot backup directory mailbox database and its subdirectories" - 06/25/2007
289123: Automatic recreation of user's mailbox account fails during restore of Exchange 2007 using Backup Exec 11d for Windows Servers Agent for Exchange - 06/19/2007
289239: Using the 11D Remote Agent for Linux and UNIX Servers, attempts to browse a directory known to have contents fails to show those contents. Also, running a backup of the directory fails with a generic access is denied error. - 06/13/2007
286144: Performing an Exchange Information Store Backup with the "Enable the restore of individual mail messages and folders from Information Store backups" selected, AND the backup job is directed to TAPE, results in a job status of failed and Access is Denied is reported in the job log. - 12/26/2006
276361: The Backup Exec Remote Agent for Linux/UNIX Servers is unable to browse directories on remote Linux/UNIX computers with filenames containing non EUC encoded characters. - 12/15/2005
256057: Common Job Log Error Codes (with Error Description) in Backup Exec 9.x, 10.x and 11d - 12/09/2003
Monday, September 17, 2007
New Exchange Server 2007 mailbox stamped as legacy mailbox
If you use the Exchange Server 2003/2000 extensions to Active Directory Users & Computers (ADUC) console to create mailboxes residing on Exchange Server 2007 servers, these mailboxes get stamped as legacy mailboxes.Exchange Server 2007 mailboxes should be created using the Exchange (2007) console or shell.To remove the legacy tag from mailboxes created using ADUC, use the following command:
Set-Mailbox "First Lastname" -ApplyMandatoryPropertiesThis is documented in KB 931747: A mailbox that is located on an Exchange Server 2007 server may be identified as a legacy mailbox in Exchange Server 2007.To get a list of legacy mailboxes:
Get-Mailbox where {$_.RecipientTypeDetails -eq "legacymailbox"}Note, not all legacy mailboxes reside on Exchange Server 2007 servers, so it's not a good idea to use the ApplyMandatoryProperties command to all of these. Mailboxes residing on Exchange Server 2003/2000 servers are also legacy mailboxes, and you may see some mailboxes moved from Exchange Server 2003/2000 servers carry this tag as well.

